Breaking News




Popular News











Enter your email address below and subscribe to our newsletter
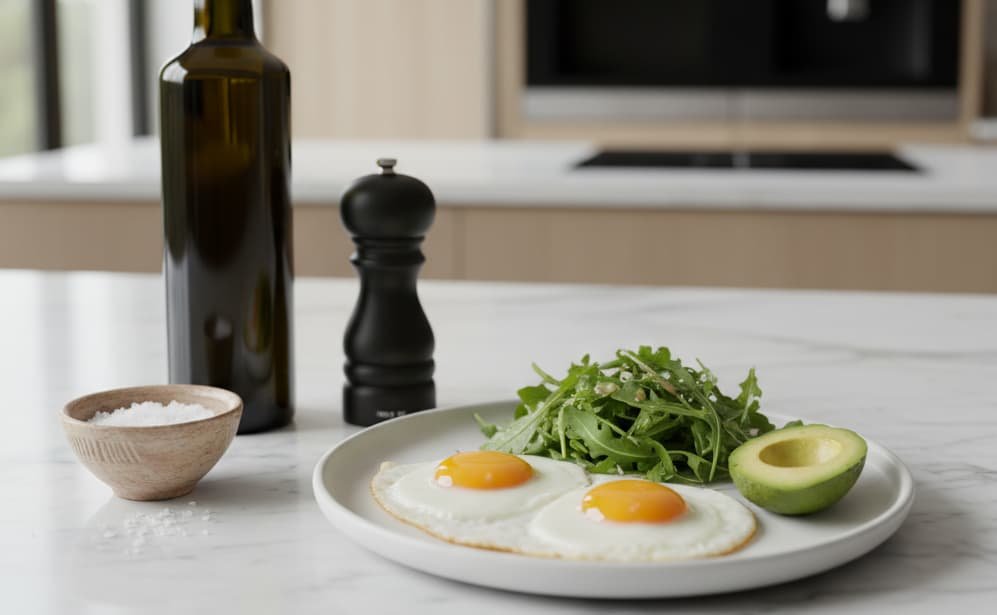

Eggs remain one of the most misunderstood foods in modern nutrition. For decades, outdated cholesterol myths created unnecessary fear around daily egg consumption, despite overwhelming evidence supporting their nutritional density, metabolic benefits, and role in long-term health. When consumed consistently and prepared properly, eggs deliver a powerful combination of protein, healthy fats, vitamins, minerals, and protective compounds that support nearly every system in the body.
Daily intake of three to four eggs provides a balanced nutritional foundation for muscle repair, brain health, hormone production, metabolic stability, immune resilience, and sustained energy. Unlike many processed protein sources, eggs offer unmatched biological efficiency, allowing the body to absorb and utilize nutrients with minimal waste. When paired with quality ingredients and prepared thoughtfully, eggs become one of the most reliable cornerstone foods for modern health optimization.
Protein quality is determined by how efficiently the body absorbs and uses amino acids for tissue repair, enzyme production, hormone synthesis, and cellular regeneration. Eggs hold the highest biological value among all natural proteins, meaning a greater percentage of their amino acids are absorbed and utilized by the body compared to meat, fish, or plant sources.
Unlike muscle meats, eggs contain both protein and fat in a naturally balanced ratio. Approximately 65 percent of the total energy from an egg can be used as fuel, making eggs uniquely efficient for metabolic stability. Lean protein alone cannot adequately fuel the body over time, which historically led to metabolic stress in diets that relied heavily on extremely lean meats.
Egg whites contain antimicrobial proteins that protect against harmful bacteria, while the yolk provides essential fats that stabilize blood sugar, support hormone balance, and promote long-lasting satiety. Cooking eggs neutralizes compounds that interfere with biotin absorption, ensuring safe daily consumption.
Egg protein also contains all essential amino acids, including leucine, which plays a central role in muscle growth and recovery. This makes eggs especially valuable for maintaining lean mass, joint integrity, and connective tissue strength across all age groups.
Eggs have been incorrectly blamed for elevating cholesterol and increasing cardiovascular risk. Modern research consistently demonstrates that dietary cholesterol has minimal impact on blood cholesterol levels for the majority of individuals. The body tightly regulates cholesterol production internally based on metabolic needs rather than food intake.
Eggs contain phospholipids that improve lipid metabolism and support healthy cell membranes. They also contain compounds that mimic natural ACE-inhibiting activity, supporting healthy blood pressure regulation. Vitamin K2 found in eggs helps direct calcium away from arteries and soft tissues toward bones and teeth, reducing long-term cardiovascular risk.
Rather than contributing to heart disease, eggs support metabolic balance, inflammation control, and vascular health when consumed as part of a nutrient-dense diet.
Eggs are one of the richest natural sources of choline, a B-vitamin critical for liver health, bile production, neurotransmitter synthesis, and DNA repair pathways. Choline supports healthy fat metabolism in the liver and helps maintain cognitive performance, memory, and focus.
Lutein and zeaxanthin, two powerful antioxidants concentrated in egg yolks, accumulate in the retina and protect against blue light damage, ultraviolet exposure, and age-related vision decline. These compounds also support neurological health beyond the eyes, contributing to cognitive clarity and neural resilience.
Eggs contain retinol, the active form of vitamin A, which supports immune defense, skin integrity, respiratory health, and digestive lining protection. Vitamin D naturally present in eggs supports immune modulation, bone density, hormonal balance, and metabolic signaling.
Phospholipids in eggs strengthen brain cell membranes, improving neural communication and cognitive performance. Together, these nutrients make eggs a foundational food for lifelong brain and nervous system health.
Egg quality directly influences nutritional value. Conventional caged eggs come from hens confined to extremely limited space, often exposed to chronic stress and nutrient-poor feed. These conditions reduce nutrient density and increase inflammatory fatty acid profiles.
Cage-free eggs provide slightly improved conditions but still limit natural movement and outdoor exposure. The highest nutritional quality comes from Pasture-Raised Eggs, where hens forage outdoors, consume insects, plants, and natural feed sources, producing eggs richer in omega-3 fats, carotenoids, and fat-soluble vitamins.
Organic labeling refers primarily to feed quality rather than living conditions. Organic pasture-raised eggs combine both advantages but may carry higher cost. When available, purchasing from local farms or trusted suppliers further improves freshness and nutrient integrity.
Egg yolk color reflects carotenoid content. Deeper orange yolks typically indicate higher nutrient density. Artificial coloring in conventional eggs can mask poor nutrition, making sourcing critical for quality assurance.
Cooking method and food pairing significantly influence nutrient absorption and metabolic response. Light cooking preserves sensitive antioxidants while improving digestibility. Overcooking can degrade certain vitamins and reduce bioavailability.
Cooking eggs in Extra Virgin Olive Oil or Grass-Fed Butter enhances fat-soluble vitamin absorption while providing additional anti-inflammatory compounds. A Cast Iron Skillet improves heat distribution and supports gentle cooking temperatures.
Pairing eggs with Organic Arugula increases phytonutrient absorption due to fat-soluble synergy. Adding onions enhances detoxification pathways, while freshly ground Black Pepper Grinder improves carotenoid bioavailability. A pinch of Sea Salt supports electrolyte balance and digestion.
Seasonal Organic Tomatoes contribute lycopene, supporting vascular health and antioxidant protection. Fresh Avocado supplies potassium, fiber, and monounsaturated fats that stabilize blood sugar and support cardiovascular function.
Avoid pairing eggs with refined carbohydrates or sugary sauces that elevate insulin and disrupt metabolic balance. Whole food combinations preserve the natural benefits of egg nutrition.
Consuming three to four eggs daily provides a robust baseline of protein, healthy fats, vitamins, and protective compounds for most adults. This intake supports muscle maintenance, cognitive performance, immune resilience, metabolic efficiency, and hormonal stability.
Individuals with higher activity levels, metabolic demands, or recovery needs may benefit from slightly higher intake, while those with smaller caloric requirements may adjust downward. The focus remains on consistency, food quality, and balanced preparation rather than rigid numbers.
Eggs function best as a primary protein source in at least one daily meal. Rotating complementary proteins throughout the week maintains dietary diversity while preserving nutritional adequacy.
Storage matters. Keep eggs refrigerated, avoid prolonged exposure to heat, and use within freshness guidelines to preserve nutrient integrity. Cracked shells should be discarded to prevent contamination.
When budget constraints exist, conventional eggs still offer superior nutrition compared to processed protein products. Nutrient density outweighs perfection when accessibility limits options.
Eggs remain one of the most complete natural foods available, delivering unmatched biological efficiency, metabolic stability, and protective nutrition. When sourced carefully, prepared intelligently, and paired with whole ingredients, daily egg consumption supports long-term health, resilience, and performance across every stage of life.