Breaking News




Popular News











Enter your email address below and subscribe to our newsletter
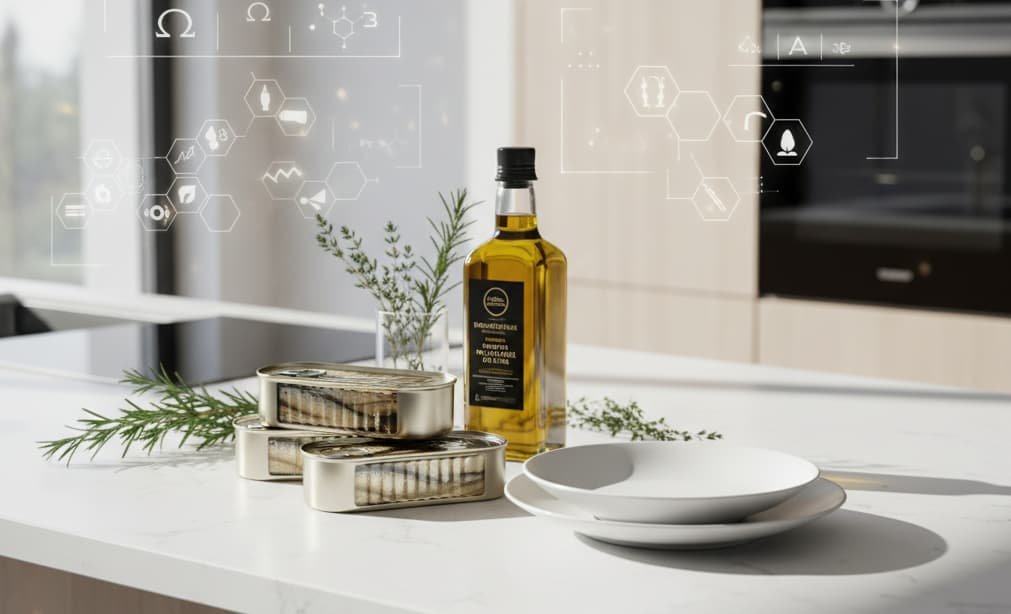

Sardine fasting is a fasting-mimicking nutrition strategy built around consuming only sardines for a short, controlled period, typically three to five days. Instead of complete calorie deprivation, the body receives highly concentrated nutrition in a minimal calorie window, allowing metabolic benefits similar to fasting while maintaining essential micronutrient intake.
Sardines deliver exceptional nutrient density per calorie. They provide complete protein, omega-3 fatty acids, fat-soluble vitamins, trace minerals, calcium from edible bones, and bioavailable micronutrients rarely found together in a single food source. When packed in extra virgin olive oil with skin and bones intact, the nutritional profile becomes even more complete.
This density allows the body to enter an energy deficit without triggering nutrient scarcity signals. Hunger remains controlled because essential biological needs are satisfied. Insulin levels fall naturally. Ketone production increases within one to two days. Metabolic switching occurs efficiently without the psychological strain of full fasting.
The strategy mimics many fasting benefits while reducing the barrier to entry. Instead of removing food entirely, food quality becomes the metabolic lever.
The body regulates hunger based on nutritional sufficiency rather than calorie quantity alone. When micronutrient requirements remain unmet, appetite persists even when calories are abundant. Sardine fasting reverses this pattern by saturating nutrient needs in minimal caloric volume.
Sardines deliver high levels of vitamin D, B12, selenium, iodine, calcium, phosphorus, zinc, and essential fatty acids. Omega-3 intake becomes exceptionally high without supplementation. DHA and EPA levels rise rapidly in circulation, improving cellular membrane fluidity, brain signaling, inflammation control, and insulin sensitivity.
Protein intake remains sufficient to preserve lean tissue while maintaining satiety. Fat content provides steady energy without glucose spikes. The combination stabilizes blood sugar, suppresses cravings, and supports sustained focus.
Many individuals experience improved mental clarity, reduced hunger variability, improved energy consistency, and enhanced productivity during sardine fasting phases. Ketone production accelerates because glucose availability remains low while fat intake remains moderate. This promotes stable brain fuel availability without the volatility associated with carbohydrate-driven energy swings.
Unlike broth fasting or juice fasting, sardine fasting avoids triggering appetite through incomplete nutrient signaling. The body receives what it needs without stimulating overconsumption.
One of the most profound effects of sardine fasting is aggressive omega-3 saturation. EPA and DHA intake rises dramatically without relying on capsules or synthetic concentrates. These fatty acids regulate inflammatory pathways, improve mitochondrial efficiency, stabilize neuronal membranes, and enhance cardiovascular signaling.
Chronic inflammation often underlies insulin resistance, cognitive fatigue, joint discomfort, and metabolic dysfunction. Omega-3 enrichment shifts the inflammatory balance toward resolution rather than chronic activation.
High-sensitivity inflammatory markers frequently decline during sardine fasting cycles. Reduced inflammatory signaling improves insulin responsiveness, accelerates fat mobilization, and supports cognitive clarity. Neural inflammation often contributes to brain fog, mood instability, and reduced motivation. Omega-3 restoration improves neurotransmitter efficiency and neural signaling stability.
Omega-3s also demonstrate muscle-sparing properties during calorie restriction. Lean tissue preservation improves while fat oxidation accelerates. This makes sardine fasting more protective of muscle mass compared to zero-calorie fasts that may elevate cortisol and increase protein breakdown in vulnerable individuals.
The anti-inflammatory impact compounds over repeated cycles, enhancing long-term metabolic resilience rather than producing only short-term weight shifts.
Traditional fasting can elevate stress hormones, disrupt sleep, and create electrolyte imbalances if not managed carefully. Sardine fasting maintains metabolic advantages while reducing physiological stress.
Calorie intake remains low enough to trigger insulin suppression and ketone production. At the same time, protein, fat, minerals, and micronutrients remain sufficient to prevent nutrient depletion signals. This allows ketosis to emerge smoothly without excessive sympathetic activation.
Ketone availability stabilizes brain energy delivery, reducing hunger volatility and emotional stress around food. Mental clarity often improves within the first 48 hours. Energy becomes more consistent rather than fluctuating with glucose availability.
Because nutrient intake remains adequate, metabolic adaptation occurs more efficiently than complete fasting for many individuals. Recovery after the fasting phase remains smoother, reducing rebound overeating risk when reintroducing normal meals.
This approach creates a metabolic reset without triggering excessive biological alarm signals.
A typical sardine fasting protocol lasts three to five days. Daily intake ranges from two to three cans of high-quality sardines divided into one or two meals. Hydration remains consistent. Electrolyte balance is naturally supported by mineral content within the fish but adequate fluid intake remains essential.
Product quality matters. Sardines should be packed in extra virgin olive oil rather than industrial seed oils. Skin and bones should remain intact to maximize calcium, collagen, fat-soluble vitamins, and trace minerals. Minimal processing preserves omega-3 integrity and nutrient stability.
Seasonings may remain simple. Salt, herbs, lemon, or mild spices can be used without adding carbohydrates or sugar. Added sauces, refined oils, or processed condiments should be avoided during the fasting window.
Physical activity should remain moderate. Walking, mobility work, light resistance training, and gentle outdoor movement support circulation and insulin sensitivity without elevating stress hormones excessively. High-intensity training may be reduced during the fasting cycle to preserve recovery capacity.
Sleep should remain prioritized. Early bedtime, hydration, and mineral intake support nervous system stability during metabolic transitions.
Refeeding after the fasting phase should remain controlled. Protein-rich, fiber-rich whole foods stabilize insulin and prevent rapid rebound. Avoiding refined carbohydrates and excessive caloric surplus during the first week preserves metabolic gains.
Consistency produces compounding benefits. Repeating sardine fasting periodically trains metabolic flexibility and improves insulin responsiveness over time.
Complete calorie restriction often triggers psychological resistance and physiological stress. Hunger hormones spike. Cortisol rises. Sleep may fragment. Electrolytes fluctuate. Mental focus may decline in early stages.
Sardine fasting reduces these barriers. Nutrient sufficiency signals remain satisfied. Satiety hormones stabilize. Blood sugar remains controlled. Ketone availability supports brain energy. The nervous system experiences less threat perception compared to full fasting.
The barrier to entry remains lower for most individuals. Eating something consistent each day reduces psychological friction while maintaining metabolic benefits.
Metabolic adaptation improves with repetition. The first cycle may feel challenging. Subsequent cycles become easier as mitochondrial efficiency increases and fat oxidation pathways strengthen. The body learns to transition between fuel sources more smoothly.
This training effect resembles metabolic conditioning rather than deprivation.
While sardines provide one of the highest nutrient density profiles per calorie, other single-food fasting approaches may also deliver metabolic benefits depending on tolerance and preference.
Egg-based fasting delivers complete protein, choline, fat-soluble vitamins, and amino acids while remaining low in carbohydrates. Some individuals experience rapid body composition improvements with short egg fasts due to nutrient density and hormonal stability.
Mackerel offers similar omega-3 density and mineral content to sardines and may serve as a viable alternative for taste variation.
Organ meats such as liver deliver exceptional micronutrient density but may require culinary preparation and careful portioning due to vitamin A concentration.
Grass-fed beef delivers protein and iron but lacks omega-3 density compared to fish-based strategies.
The principle remains consistent: maximize nutrient density while maintaining a controlled energy deficit to trigger insulin reduction and metabolic switching.
Sardine fasting functions as metabolic conditioning rather than a temporary diet. Each cycle improves insulin sensitivity, reduces inflammatory load, enhances fat oxidation capacity, and strengthens metabolic flexibility.
Repeated exposure trains the body to switch fuels efficiently. Hunger regulation improves. Energy stability increases. Craving patterns normalize. Body composition gradually shifts toward improved fat utilization without aggressive calorie manipulation.
The objective is not extreme restriction. The objective is restoring biological signaling efficiency so the body naturally regulates energy balance, inflammation, and metabolic health.
When nutrient density increases and insulin signaling stabilizes, the body exits survival mode and resumes optimal self-regulation. Fat loss becomes effortless rather than forced. Mental clarity improves. Recovery capacity strengthens.
Sardine fasting demonstrates how intelligent nutrition density can outperform deprivation-based dieting while supporting long-term metabolic resilience and sustainability.